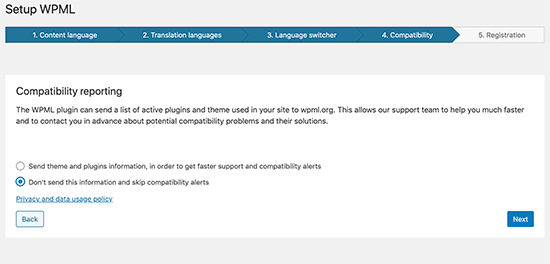
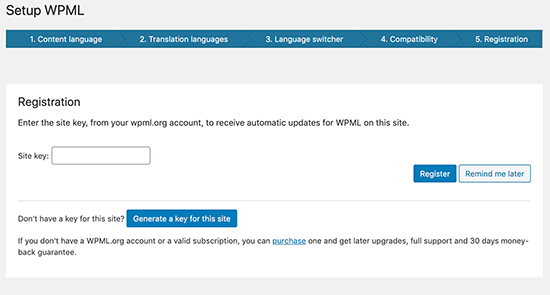
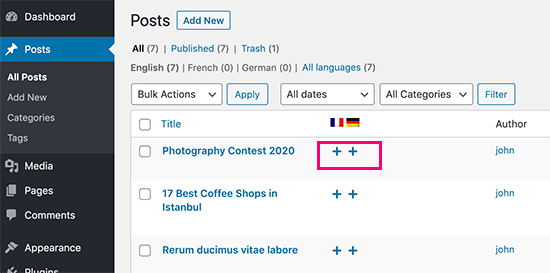
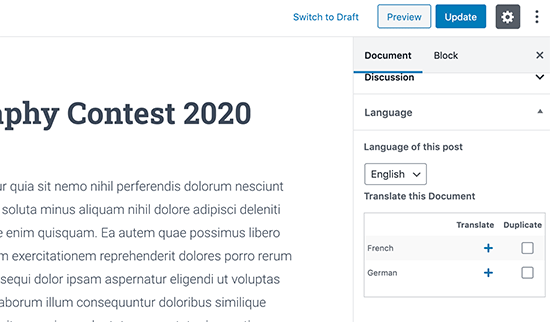
Multilingual content development presents its own set of difficulties, necessitating close attention to language translations and the use of the right tools. The exciting part is that translation technology has advanced remarkably over time.
In this article, we’ll explore the growth of translation technology throughout time, as well as its origins, and lead up to whether machine translation and artificial intelligence (AI) actually outperform their conventional counterparts when it comes to managing translations. In the process, we’ll discuss the fascinating opportunities offered by automated approaches to language translation as we examine their advantages and potential drawbacks.
And finally, we will speculate on the future of language translation, specifically the exhilarating showdown between OpenAI and Google in their race to dominate the AI landscape.
The Evolution Of Translation TechnologyTranslation technology can be traced back to Al-Kindi’s Manuscript on Deciphering Cryptographic Messages. However, with the arrival of computers in the mid-twentieth century, translation technology began taking shape. Over the years, significant milestones have marked the evolution, shaping how translations are performed and enhancing the capabilities of language professionals.

Georgetown University and IBM conducted the so-called Georgetown-IBM experiment in the 1950s. The experiment was designed primarily to capture governmental and public interests and funding by demonstrating machine translation capabilities. It was far from a fully featured system. This early system, however, was rule-based and lexicographical, resulting in low reliability and slow translation speeds. Despite its weaknesses, it laid the foundation for future advancements in the field.
The late 1980s and early 1990s marked the rise of statistical machine translation (SMT) pioneered by IBM researchers. By leveraging bilingual corpora, SMT improved translation accuracy and laid the groundwork for more advanced translation techniques.
In the early 1990s, commercial computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools became widely available, empowering translators and boosting productivity. These tools utilized translation memories, glossaries, and other resources to support the translation process and enhance efficiency.
The late 1990s saw IBM release a rule-based statistical translation engine (pdf), which became the industry standard heading into the new century. IBM’s translation engine introduced predictive algorithms and statistical translation, bringing machine translation to the forefront of language translation technology.
In the early 2000s, the first cloud-based translation management systems (TMS) began appearing in the market. While there were some early non-cloud-based versions in the mid-1980s, these modern systems transformed the translation process by allowing teams of people to work more flexibly and collaborate with other company members regardless of their location. The cloud-based approach improved accessibility, scalability, and collaboration capabilities, completely changing how translation projects were managed.
2006 is a significant milestone in translation management because it marks the launch of Google Translate. Using predictive algorithms and statistical translation, Google Translate brought machine translation to the masses and has remained the de facto tool for online multilingual translations. Despite its powerful features, it gained a reputation for inaccurate translations. Still, it plays a pivotal role in making translation technology more widely known and utilized, paving the way for future advancements.

In 2016, Google Translate made a significant leap by introducing neural machine translation (NMT). NMT surpassed previous translation tools, offering improved quality, fluency, and context preservation.
NMT set a new commercial standard and propelled the field forward. By 2017, DeepL emerged as an AI-powered machine translation system renowned for its high-quality translations and natural-sounding output. DeepL’s capabilities further demonstrated the advancements achieved in the field of translation technology.
From 2018 onward, the focus has remained on enhancing NMT models, which continue to outperform traditional statistical machine translation (SMT) approaches. NMT has proven instrumental in improving translation accuracy and has become the preferred approach in today’s many translation applications.
What Translation Technology Came Into Place Over the YearsTranslation technology has evolved significantly over the years, offering various tools to enhance the translation process. The main types of translation technology include:
- Computer-assisted translation (CAT)
These software applications support translators by providing databases of previous translations, translation memories, glossaries, and advanced search and navigation tools. CAT tools revolutionize translation by improving efficiency and enabling translators to focus more on the translation itself. - Machine translation (MT)
Machine translation is an automated system that produces translated content without human intervention. It can be categorized into rule-based (RBMT), statistical (SMT), or neural (NMT) approaches. MT’s output quality varies based on language pairs, subject matter, pre-editing, available training data, and post-editing resources. Raw machine translation may be used for low-impact content while post-editing by human translators is advisable for high-impact or sensitive content. - Translation management systems (TMS)
TMS platforms streamline translation project management, offering support for multiple languages and file formats, real-time collaboration, integration with CAT tools and machine translation, reporting features, and customization options. TMS solutions ensure organized workflow and scalability for efficient translation project handling.
Translation technology advancements have transformed the translation process, making it more efficient, cost-effective, and scalable.
Finding The Right Translation Approach: Machine Vs. HumanFinding the proper translation approach involves weighing the benefits and drawbacks of machine translation (MT) and human translation. Each approach has its own strengths and considerations to take into account.
Human translation, performed by professional linguists and subject-matter experts, offers accuracy, particularly for complex documents like legal and technical content. Humans can grasp linguistic intricacies and apply their own experiences and instincts to deliver high-quality translations. They can break down a language, ensure cultural nuances are correctly understood, and inject creativity to make the content compelling.
Collaborating with human translators allows direct communication, reducing the chances of missing project objectives and minimizing the need for revisions.

That said, human translation does have some downsides, namely that it is resource-intensive and time-consuming compared to machine translation. If you have ever worked on a multilingual project, then you understand the costs associated with human translation — not every team has a resident translator, and finding one for a particular project can be extremely difficult. The costs often run high, and the process may not align with tight timelines or projects that prioritize speed over contextual accuracy.
Nevertheless, when it comes to localization and capturing the essence of messaging for a specific target audience, human translators excel in fine-tuning the content to resonate deeply. Machine translation cannot replicate the nuanced touch that human translators bring to the table.
On the other hand, machine translation — powered by artificial intelligence and advanced algorithms — is rapidly improving its understanding of context and cultural nuances. Machine translation offers speed and cost-efficiency compared to that manual translations, making it suitable for certain projects that prioritize quick turnarounds and where contextual accuracy is not the primary concern.
Modern TMSs often integrate machine and human translation capabilities, allowing users to choose the most appropriate approach for their specific requirements. Combining human translators with machine translation tools can create a powerful translation workflow. Machine translation can be used as a starting point and paired with human post-editing to ensure linguistic precision, cultural adaptation, and overall quality.
Translation management systems often provide options for leveraging both approaches, allowing for flexibility and optimization based on the content, time constraints, budget, and desired outcome. Ultimately, finding the proper translation approach depends on the content’s nature, the desired accuracy level, project objectives, budget considerations, and time constraints. Assessing these factors and considering the advantages and disadvantages of human and machine translation will guide you in making informed decisions that align with your or your team’s needs and goals.
AI and Machine TranslationThanks to machine learning and AI advancements, translation technology has come a long way in recent years. However, complete translation automation is not yet feasible, as human translators and specialized machine translation tools offer unique advantages that complement each other.
The future of translation lies in the collaboration between human intelligence and AI-powered machine translation. Human translators excel in creative thinking and adapting translations for specific audiences, while AI is ideal for automating repetitive tasks.
This collaborative approach could result in a seamless translation process where human translators and AI tools work together in unison.
Machine-translation post-editing ensures the accuracy and fluency of AI-generated translations, while human translators provide the final touches to cater to specific needs. This shift should lead to a transition from computer-assisted human translation to human-assisted computer translation. Translation technology will continue to evolve, allowing translators to focus on more complex translations while AI-powered tools handle tedious tasks. It is no longer a question of whether to use translation technology but which tools to utilize for optimal results.
The future of translation looks promising as technology empowers translators to deliver high-quality translations efficiently, combining the strengths of human expertise and AI-powered capabilities.
The Rise of Translation Management SystemsRegarding AI and human interaction, TMSs play a crucial role in facilitating seamless collaboration. Here are five more examples of how TMSs enhance the synergy between human translators and AI.
Terminology Management
TMSs offer robust terminology management features, allowing users to create and maintain comprehensive term bases or glossaries, ensuring consistent usage of specific terminology across translations, and improving accuracy.
Quality Assurance Tools
TMSs often incorporate quality assurance tools that help identify potential translation errors and inconsistencies. These tools can flag untranslated segments, incorrect numbers, or inconsistent translations, enabling human translators to review and rectify them efficiently.
Workflow Automation
TMSs streamline the translation process by automating repetitive tasks. They can automatically assign translation tasks to appropriate translators, track progress, and manage deadlines. This automation improves efficiency and allows human translators to focus more on the creative aspects of translation, like nuances in the voice and tone of the content.
Collaboration And Communication
TMSs provide collaborative features that enable real-time communication and collaboration among translation teams. They allow translators to collaborate on projects, discuss specific translation challenges, and share feedback, fostering a cohesive and efficient workflow.
Reporting And Analytics
TMSs offer comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities, providing valuable insights into translation projects. Users can track project progress, measure translator productivity, and analyze translation quality, allowing for continuous improvement and informed decision-making.
By leveraging the power of translation management systems, the interaction between AI and human translators becomes more seamless, efficient, and productive, resulting in high-quality translations that meet the specific needs of each project.
Google And OpenAI CompetitionWe’re already seeing brewing competition between Google and OpenAI for dominance in AI-powered search and generated content. I expect 2024 to be the year that the clash involves translation technology.

That said, when comparing OpenAI’s platform to Google Translate or DeepL, it’s important to consider the respective strengths and areas of specialization of each one. Let’s briefly consider the strengths of each one to see precisely how they differ.
Continuously Improved And Robust Translation
Google Translate and DeepL are dedicated to the field of machine translation and have been, for many years, focusing on refining their translation capabilities.
As a result, they have developed robust systems that excel in delivering high-quality translations. These platforms have leveraged extensive data and advanced techniques to improve their translation models, addressing real-world translation challenges continuously. Their systems’ continuous refinement and optimization have allowed them to achieve impressive translation accuracy and fluency.
Generating Text
OpenAI primarily focuses on generating human-like text and language generation tasks.
While OpenAI’s models, including ChatGPT, can perform machine translation tasks, they may not possess the same level of specialization and domain-specific knowledge as Google Translate and DeepL.
The primary objective of OpenAI’s language models is to generate coherent and contextually appropriate text rather than specifically fine-tuning their models for machine translation.
Compared to ChatGPT, Google Translate and DeepL excel in domain-specific sentences while factoring in obstacles to translation, such as background sounds when receiving audio input. In that sense, Google Translate and DeepL have demonstrated their ability to handle real-world translation challenges effectively, showcasing their continuous improvement and adaptation to different linguistic contexts.
The Future Of Machine TranslationOverall, when it comes to machine translation, Google Translate and DeepL have established themselves as leaders in the field, with a focus on delivering high-quality translations. Their extensive experience and focus on continual improvement contribute to their reputation for accuracy and fluency. While OpenAI’s ChatGPT models technically offer translation capabilities, they may not possess the same level of specialization or optimization tailored explicitly for machine translation tasks.
It’s important to note that the landscape of machine translation is continuously evolving, and the relative strengths of different platforms may change over time. While Google Translate and DeepL have demonstrated their superiority in translation quality, it’s worth considering that OpenAI’s focus on language generation and natural language processing research could benefit future advancements in their machine translation capabilities. Together, the three systems could make a perfect trifecta of accurate translations, speed and efficiency, and natural language processing.
OpenAI’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of AI technology and its track record of innovation suggests it may invest more resources in improving machine translation performance. As OpenAI continues to refine its models and explore new approaches, there is a possibility that it could bridge that gap and catch up with Google Translate and DeepL in terms of translation quality and specialization.
The machine translation landscape is highly competitive, with multiple research and industry players continuously striving to enhance translation models. As advancements in machine learning and neural networks continue, it’s conceivable that newer platforms or models could emerge and disrupt the current dynamics, introducing even higher-quality translations or specialized solutions in specific domains.
So, even though Google Translate and DeepL currently hold an advantage regarding translation quality and domain-specific expertise today in 2023, it’s essential to acknowledge the potential for future changes in the competitive landscape in the years to come. As technology progresses and new breakthroughs occur, the relative strengths and weaknesses of different platforms may shift, leading to exciting developments in the field of machine translation.
ConclusionIn summary, the evolution of translation technology has brought advancements to the multilingual space:
- The choice of translation approach depends on project requirements, considering factors such as accuracy, budget, and desired outcomes.
- Machine translation offers speed and cost-efficiency, while human translation excels in complex content.
- Collaboration between human translators and AI-powered machines is best to get accurate translations that consider voice and tone.
- Translation management systems are crucial in facilitating collaboration between AI and human translators.
While Google Translate and DeepL have demonstrated higher translation quality and specialization, OpenAI’s focus on human-like text generation may lead to improvements in machine translation capabilities. And those are only a few of the providers.
That means the future of translation technology is incredibly bright as platforms, like locize, continue to evolve. As we’ve seen, there are plenty of opportunities to push this field further, and the outcomes will be enjoyable to watch in the coming years.
Further Reading On SmashingMag
- “How AI Technology Will Transform Design,” Nick Babich & Gleb Kuznetsov
- “Using AI To Detect Sentiment In Audio Files,” Joas Pambou
- “The Rise Of Intelligent Conversational UI,” Burke Holland
- “The Future Of Design: Human-Powered Or AI-Driven?,” Keima Kai