Introduction
We are familiar with spell checkers. For most spell checkers, a candidate word is considered to be spelled correctly if it is found in a long list of valid words called a dictionary. Google provides a more powerful spell corrector for validating the keywords we type into the input text box. It checks against a dictionary. If it doesn’t find the keyword in the dictionary, it suggests a most likely replacement. To do this it associates with every word in the dictionary a frequency, the number of the times that word is expected to appear in a large document. When a word is misspelled (i.e. it is not found in the dictionary) Google suggests a “similar” word whose frequency is larger or equal to any other “similar” word. In this post, I will introduce the approach of how to implement spell autocorrect. It includes
- Trie
- Edit distance
- Nested HashMap
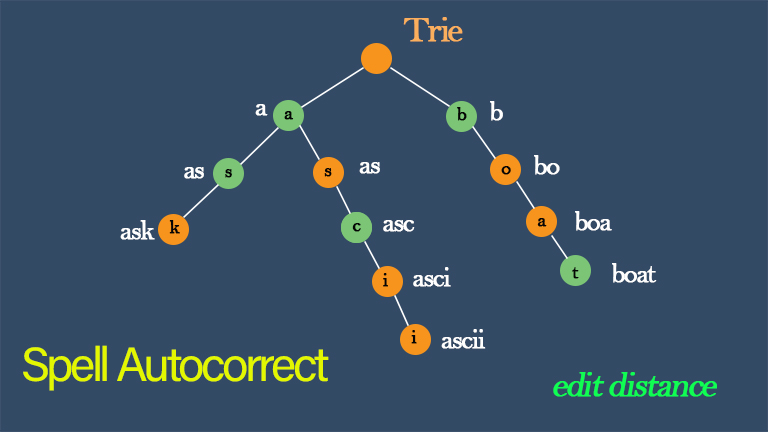
Trie (Data Structure)
For this program, we need a dictionary similar to Google’s. Our dictionary is generated using a large text file. The text file contains a large number of unsorted words. Every time our program runs it will create the dictionary from this text file. The dictionary will contain every word in the text file and a frequency for that word.