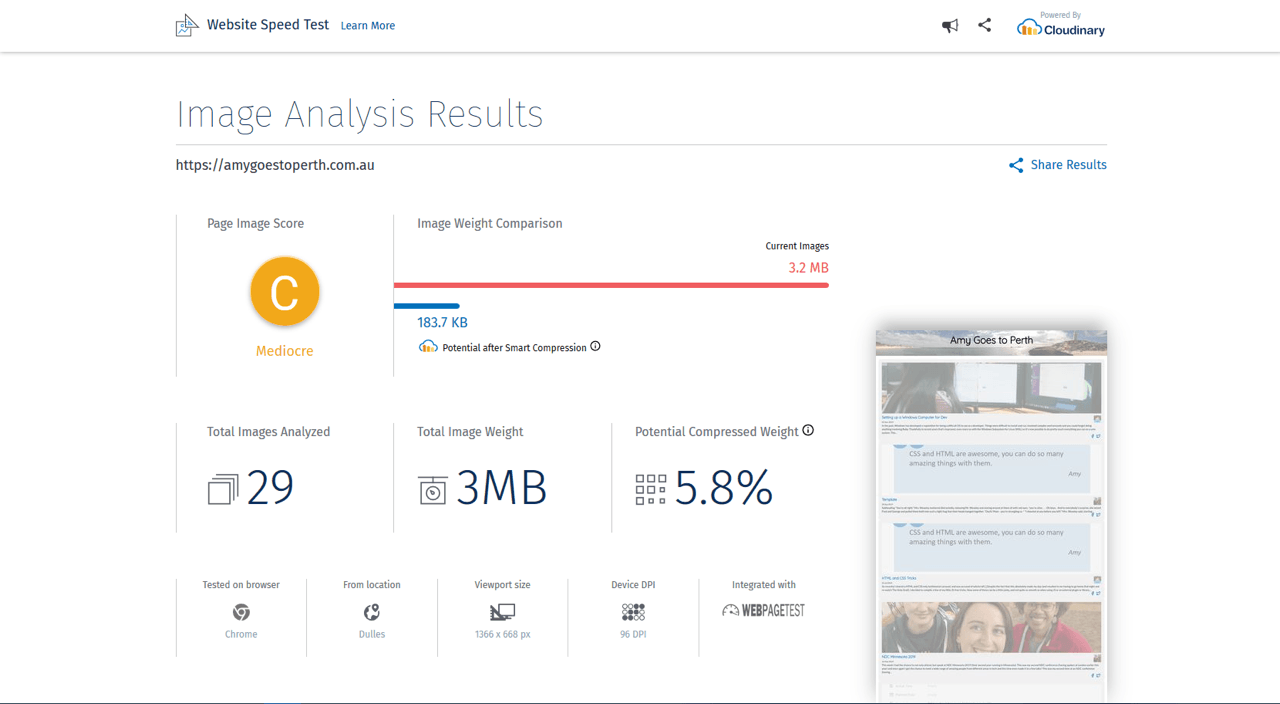
Mandy Michael turns the corner on our variable font adventure and stumbles into a grotto of wonder and amazement. Not forgetting the need for a proper performance budget, Mandy shows how variable fonts can free your creativity from bygone technical constraints.
If you read Jason’s introductory article about variable fonts, you’ll understand the many benefits and opportunities that they offer in modern web development. From this point on we’ll assume that you have either read Jason’s introduction or have some prior knowledge of variable fonts so we can skip over the getting started information. If you haven’t read up on variable fonts before jump over to “Introduction to Variable Fonts: Everything you thought you knew about fonts just changed” first and then come join me back here so we can dive into using variable fonts for interactivity and animations!
Creative Opportunities
If we can use variable fonts to improve the performance of our websites while increasing the amount of style variations available to us, it means that we no longer need to trade off design for performance. Creativity can be the driving force behind our decisions, rather than performance and technical limitations.

My goal is to demonstrate how to create interactive, creative text on the web by combining variable fonts with CSS and JavaScript techniques that you may already be familiar with. With the introduction of variable fonts, designs which would have previously been a heavy burden on performance, or simply impossible due to technical limitations, are now completely possible.
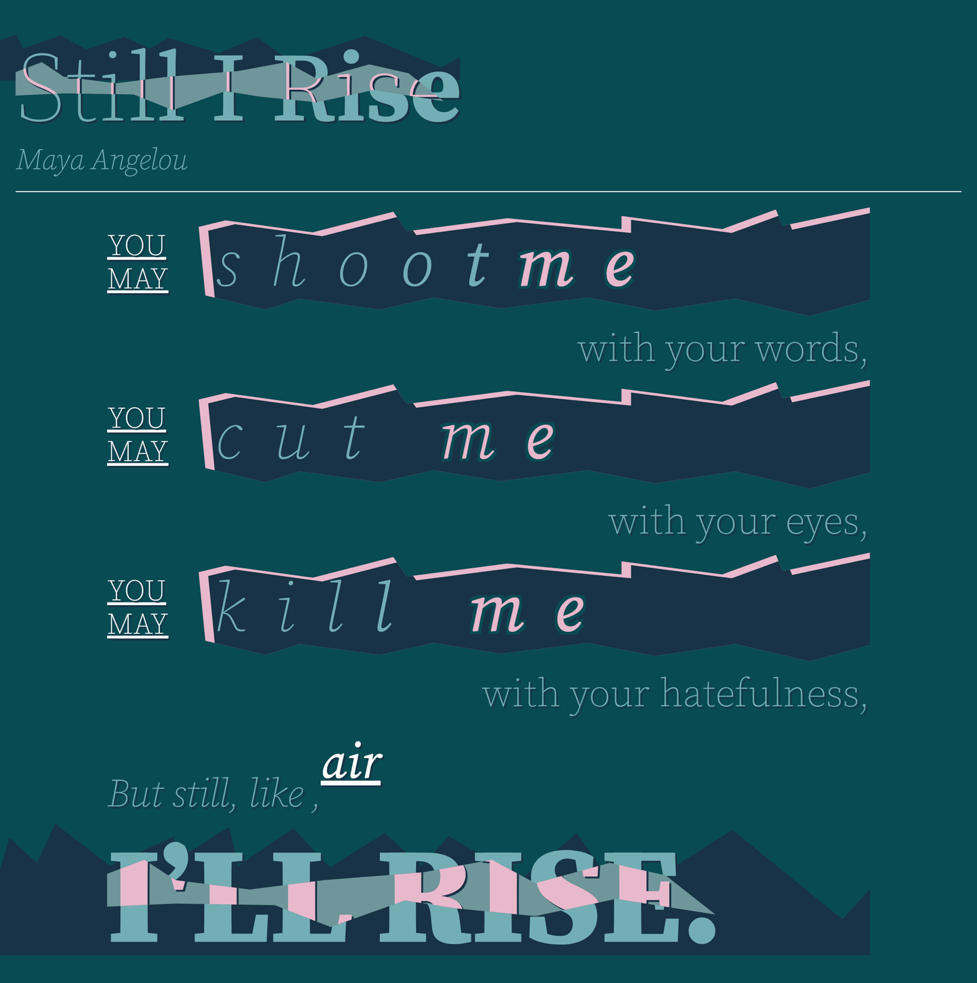

The tone and intent of our words can be more effectively represented with less worry over the impacts of loading in “too many font weights” (or other styles). This means that we can start a new path and focus on representing the content in more meaningful ways. For example, emphasising different words, or phrases depending on their importance in the story or content.
Note: using variable fonts does not negate the need for a good web font performance strategy! This is still important, because after all, they are still fonts. Keep that in mind and check out some of the great work done by Monica Dinculescu, Zach Leatherman or this incredible article by Helen Homes.
Variable Fonts & Animations
Because variable fonts can have an interpolated range of values we can leverage the flexibility and interactive nature of the web. Rather than using SVG, videos or JavaScript to accomplish these effects, we can create animations or transitions using real text, and we can do this using techniques we may already be familiar with. This means we can have editable, selectable, searchable, copy-pastable text, which is accessible via a screenreader.
Grass Variable Font Demo
This effect is achieved using a font called Decovar, by David Berlow. To achieve the animation effect we only need a couple of things to get started.
First, we set up the font-family and make use of the new property font-variation-settings to access the different axes available in Decovar.
h1 {
font-family: "Decovar";
font-variation-settings: 'INLN' 1000, 'SWRM' 1000;
}For this effect, we use two custom axis – the first is called “inline” and is represented by the code INLI and the second is “skeleton worm” represented by the code SWRM. For both axes, the maximum value is 1000 and the minimum value is 0. For this effect, we’ll make the most of the full axis range.
Once we have the base set up, we can create the animation. There are a number of ways to animate variable fonts. In this demo, we’ll use CSS keyframe animations and the font-variation-settings property, but you can also use CSS transitions and JavaScript as well.
The code below will start with the “leaves” expanded and then shrink back until it disappears.
@keyframes grow {
0% {
font-variation-settings: 'INLN' 1000, 'SWRM' 1000;
}
100% {
font-variation-settings: 'INLN' 1000, 'SWRM' 0;
}
}Once we have created the keyframes we can add the animation to the h1 element, and that is the last piece needed in order to create the animation.
h1 {
font-family: "Decovar";
font-variation-settings: 'INLN' 1000, 'SWRM' 1000;
animation: grow 4s linear alternate infinite;
}What this demonstrates is that typically, to accomplish effects like this, the heavy lifting is done by the font. We really only need a few lines of CSS for the animation, which if you think about it, is pretty incredible.
There are all sorts of interesting, creative applications of variable fonts, and a lot of incredible fonts you can make the most of. Whether you want to create that “hand-writing” effect that we often see represented with SVG, or something a little different, there are a lot of different options.
Duos Writer: Hand Writing
Decovar: Disappearing Text
See the Pen CSS-only variable font demo using Decovar Regular by Mandy Michael (@mandymichael) on CodePen.
Cheee: Snow Text
Variable Fonts, Media Queries and Customisation
It’s not that these are just beautiful or cool effects, what they demonstrate is that as developers and designers we can now control the font itself and that that means is that variable fonts allow typography on the web to adapt to the flexible nature of our screens, environments and devices.
We can even make use of different CSS media queries to provide more control over our designs based on environments, light contrast and colour schemes.
Though the CSS Media Queries Level 5 Spec is still in draft stages, we can experiment with the prefers-color-scheme (also known as dark mode) media query right now!
Dark Mode featuring Oozing Cheee by OhNoTypeCo
The above example uses a font called “Cheee” by OhNoTypeCo and demonstrates how to make use of a CSS Transition and the prefers-color-scheme media query to transition the axis of a variable font.
h1 {
font-family: “Cheee"
font-variation-settings: "TEMP" 0;
transition: all 4s linear;
}
@media (prefers-color-scheme: dark) {
h1 {
font-variation-settings: "TEMP" 1000;
}
}Dark mode isn’t just about changing the colours, it’s important to consider things like weight as well. It’s the combination of the weight, colour and size of a font that determines how legible and accessible it is for the user. In the example above, I’m creating a fun effect – but more practically, dark mode allows us to modify the contrast and styles to ensure better legibility and usability in different environments.
What is even more exciting about variable fonts in this context is that if developers and designers can have this finer control over our fonts to create more legible, accessible text, it also means the user has access to this as well. As a result, users that create their own stylesheets to customise the experience to their specific requirements, can now adjust the pages font weight, width or other available axis to what best suits them. Providing users with this kind of flexibility is such an incredible opportunity that we have never had before!
As CSS develops, we’ll have access to different environmental and system features that allow us to take advantage of our users unique circumstances. We can start to design our typography to adjust to things like screen width - which might allow us to tweak the font weight, width, optical size or other axes to be more readable on smaller or larger screens. Where the viewport is wide we can have more detail, when its smaller in a more confined space we might look at reducing the width of the font—this helps to maintain the integrity of the design as the viewport gets smaller or, to fit text into a particular space.
See the Pen CSS is Awesome - Variable fonts Edition. by Mandy Michael (@mandymichael) on CodePen.
We have all been in the situation where we just need the text to be slightly narrower to fit within the available space. If you use a variable font with a width axis you can slightly modify the width to adjust to the space available, and do so in a way that the font was designed to do, rather than using things like letter spacing which doesn’t consider the kerning of the characters.
Variable Fonts, JavaScript and Interactive Effects
We can take these concepts even further and mix in a little JavaScript to make use of a whole suite of different interactions, events, sensors and apis. The best part about this is whether you are using device orientation, light sensors, viewport resizes, scroll events or mouse movement, the base JavaScript doesn’t really change.
To demonstrate this, we’ll use a straightforward example – we’ll match our font weight to the size of our viewport – as the viewport gets smaller, the font weight gets heavier.
We’ll start off by setting our base values. We need to define the minimum and maximum axis values for the font weight, and the minimum and maximum event range, in this case the viewport size. Basically we’re defining the start and end points for both the font and the event.
// Font weight axis range
const minAxisValue = 200
const maxAxisValue = 900
// Viewport range
const minEventValue = 320px
const maxEventValue = 1440pxNext we determine the current viewport width, which we can access with something like window.innerWidth.
// Current viewport width
const windowWidth = window.innerWidthUsing the current viewport width value, we create the new scale for the viewport, so rather than the pixels values we convert it to a range of 0 - 0.99.
const windowSize = (windowWidth - minEventValue) / (maxEventValue - minEventValue)
// Outputs a value from 0 - 0.99We then take that new viewport decimal value and use it to determine the font weight based on viewport scale.
const fontWeight = windowSize * (minAxisValue - maxAxisValue) + maxAxisValue;
// Outputs a value from 200 - 900 including decimal placesThis final value is what we use to update our CSS. You can do this however you want – lately I like to use CSS Custom Properties. This will pass the newly calculated font weight value into our CSS and update the weight as needed.
// JavaScript
p.style.setProperty("--weight", fontWeight);Finally, we can put all this inside a function and inside an event listener for window resize. You can modify this however you need to in order to improve performance, but in essence, this is all you need to achieve the desired outcome.
function fluidAxisVariation() {
// Current viewport width
const windowWidth = window.innerWidth
// Get new scales for viewport and font weight
const viewportScale = (windowWidth - 320) / (1440 - 320);
const fontWeightScale = viewportScale * (200 - 900) + 900;
// Set in CSS using CSS Custom Property
p.style.setProperty("--weight", fontWeightScale);
}
window.addEventListener("resize", fluidAxisVariation);You can apply this to single elements, or multiple. In this case, I’m changing the paragraph font weights and different rates, but also reducing the width axis of the headline so it doesn’t wrap onto multiple lines.
As previously mentioned, this code can be used to create all sorts of really amazing, interesting effects. All that’s required is passing in different event and axis values.
In the following example, I’m using mouse position events to change the direction and rotation of the stretchy slinky effect provided by the font “Whoa” by Scribble Tone.
See the Pen Slinky Text - WHOA Variable font demo by Mandy Michael (@mandymichael) on CodePen.
We can also take the dark mode/colour schemes idea further by making use of the Ambient Light Sensor to modify the font to be more legible and readable in low light environments.
This effect uses Tiny by Jack Halten Fahnestock from Velvetyne Type Foundry and demonstrates how we modify our text based by query the characteristics of the user’s display or light-level, sound or other sensors.
It’s only because Variable fonts give us more control over each of these elements that we can fine-tune the font characteristics to maximise the legibility, readability and overall accessibility of our website text. And while these examples might seem trivial, they are great demonstrations of the possibilities. This is a level of control over our fonts and text that is unprecedented.
Variable Fonts offer a new world of interactivity, usability and accessibility, but they are still a new technology. This means we have the opportunity to figure out how and what we can achieve with them. From where I stand, the possibilities are endless, so don’t be limited by what we can already do – the web is still young and there is so much for us to create. Variable fonts open up doors that never existed before and they give us an opportunity to think more creatively about how we can create better experiences for our users.
At the very least, we can improve the performance of our websites, but at best, we can make more usable, more accessible, and more meaningful content - and that, is what gets me really excited about the future of web typography with variable fonts.
About the author
Mandy is a community organiser, speaker, and developer working as the Front End Development Manager at Seven West Media in Western Australia. She is a co-organiser and Director of Mixin Conf, and the founder and co-organiser of Fenders, a local meetup for front-end developers providing events, mentoring and support to the Perth web community.
Mandy’s passion is CSS, HTML and JS and hopes to inspire that passion in others. She loves the supportive and collaborative nature of the web and strives to encourage this environment through the community groups she is a part of. Her aim is to create a community of web developers who can share, mentor, learn and grow together.